Microbiological Research Methods
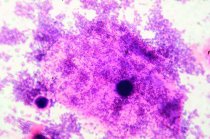
MICROBIOLOGICAL METHODS
The purpose of the microbiological study is to establish the ethical role of microorganisms in the event of disease or clinical syndrome. It should be borne in mind that inflammatory processes of the reproductive system can be found as a PKO, a transit component normal microflora vaginas and other biotops, as well as absolute pathogens, are propellers of STIs. This link between STIs and opportunistic infections (accounted by MIP) determines the need for an integrated approach to microbiological diagnostics.
POINT
Microbiological research methods are used to confirm or eliminate infectious diseases.
RULES OF CLINICAL MATERIAL
Divided from the wind are taken by a plastic one-time sterile bacteriological lounge with 1 ml or a thin dacron tampon on aluminium wire. The pre-exterior retrieval should be cleaned with a blank or cotton tampon. In the absence of visible releases, a doctor can perform a light ureth massage. The tampon/heart shall be inserted in the wind by 1 to 2 cm and removed with a slight push on the side and rear walls.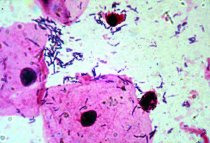 For microscopic and immunofluorescent research, material is transported to an object glass by rolling a tampon or moving a loop with a lung-pressure material. For cultural research and PCR, the material shall be placed in probes with the relevant vehicles.
For microscopic and immunofluorescent research, material is transported to an object glass by rolling a tampon or moving a loop with a lung-pressure material. For cultural research and PCR, the material shall be placed in probes with the relevant vehicles.
Outside floors, vagina presupposing: masks are taken by sterile cotton tampons with pathologically altered plots; in the inflammation of the large iron, the prediction is carried out with punkium, when the abscess is opened, the iron is taken by a gene sterile wat.
Vagina: After the introduction of the mirror and the lift, the sterile wattt tampon removed from the rear or from the pathologically altered slimy casing areas; for cultural purposes, tampon is placed in a sterile test and immediately sent to the laboratory. If this requirement cannot be met, the sample shall be placed in a sample with the transport environment.